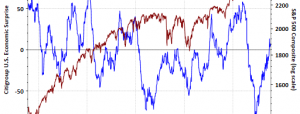
There can be little doubt that data releases rather than experience or intuition are driving the economic conversation. This is perhaps a function of the disconnection that many people feel about an economy that they no longer understand. Rather than trusting their own eyes or their own gut to form an opinion, it’s much easier to grab a set of convenient numbers. The big question then becomes what numbers you choose to look at and which you choose to ignore.
While there are a great many types of economic data releases, issued by a myriad of public and private sources, two reports have risen above the rest in importance: the Quarterly GDP estimates issued by the Bureau of Economic Analysis, and the monthly jobs report issued by the Bureau of Labor Statistics. And those two reports have been recently coming up roses. The 3rd quarter GDP growth report, released on November 25th, revised growth upwards to an annualized rate of 3.9%, and the November Jobs report, released on December 5th, showed the creation of 321,000 new jobs in November, the highest monthly total in nearly three years. These reports have solidified the views of the mass of analysts that the U.S. economy is currently firing on all cylinders.
But to make this conclusion, almost all the other data sets, which used to be considered significant, have been either ignored or, when that proves impossible, rationalized away to make the figures unimportant. This never happens with strong data, which is typically accepted at face value.
In the weeks leading up to, and the days after, the recent GDP and jobs reports, a torrent of data releases came in that were almost universally awful. However, in our current era of journalistic lethargy, these reports have received almost no attention at all.
While it would be too long and boring to list all of these moribund statistics, here is a brief overview, in chronological order, of what you are likely not hearing:
November 24 – The Chicago Fed National Activity Index, which weighs 85 different economic indicators to gauge the national economy, fell to 0.14 in October from 0.29 in September. The three-month average declined to negative 0.01 from positive 0.12. The index is designed so that readings above zero indicate above-trend growth.